Error Link
Handle and inspect errors in your GraphQL network stack.
Overview
Use this link to perform some custom logic when a GraphQL or network error happens:
import { onError } from "@apollo/client/link/error";
const link = onError(({ graphQLErrors, networkError }) => {
if (graphQLErrors)
graphQLErrors.map(({ message, locations, path }) =>
console.log(
`[GraphQL error]: Message: ${message}, Location: ${locations}, Path: ${path}`
)
);
if (networkError) console.log(`[Network error]: ${networkError}`);
});Callback
The Error link takes a function that is called in the event of an error. This function is called with an object containing the following keys:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
operation | The Operation that errored |
response | The result returned from lower down in the link chain |
graphQLErrors | An array of errors from the GraphQL endpoint |
networkError | Any error during the link execution or server response, that wasn't delivered as part of the errors field in the GraphQL result |
forward | A reference to the next link in the chain. Calling return forward(operation) in the callback will retry the request, returning a new observable for the upstream link to subscribe to. |
Returns: Observable<FetchResult> | void The error callback can optionally return an observable from calling forward(operation) if it wants to retry the request. It should not return anything else.
Error categorization
An error is passed as a networkError if a link further down the chain called the error callback on the observable. In most cases, graphQLErrors is the errors field of the result from the last next call.
A networkError can contain additional fields, such as a GraphQL object in the case of a failing HTTP status code. In this situation, graphQLErrors is an alias for networkError.result.errors if the property exists.
Retrying failed requests
An error handler might want to do more than just logging errors. You can check for a certain failure condition or error code, and retry the request if rectifying the error is possible. For example, when using some form of token based authentication, there is a need to handle re-authentication when the token expires. Here is an example of how to do this using forward():
onError(({ graphQLErrors, networkError, operation, forward }) => {
if (graphQLErrors) {
for (let err of graphQLErrors) {
switch (err.extensions.code) {
case 'UNAUTHENTICATED':
// error code is set to UNAUTHENTICATED
// when AuthenticationError thrown in resolver
// modify the operation context with a new token
const oldHeaders = operation.getContext().headers;
operation.setContext({
headers: {
...oldHeaders,
authorization: getNewToken(),
},
});
// retry the request, returning the new observable
return forward(operation);
}
}
}
if (networkError) {
console.log(`[Network error]: ${networkError}`);
// if you would also like to retry automatically on
// network errors, we recommend that you use
// @apollo/client/link/retry
}
});Here is a diagram of the request flow:
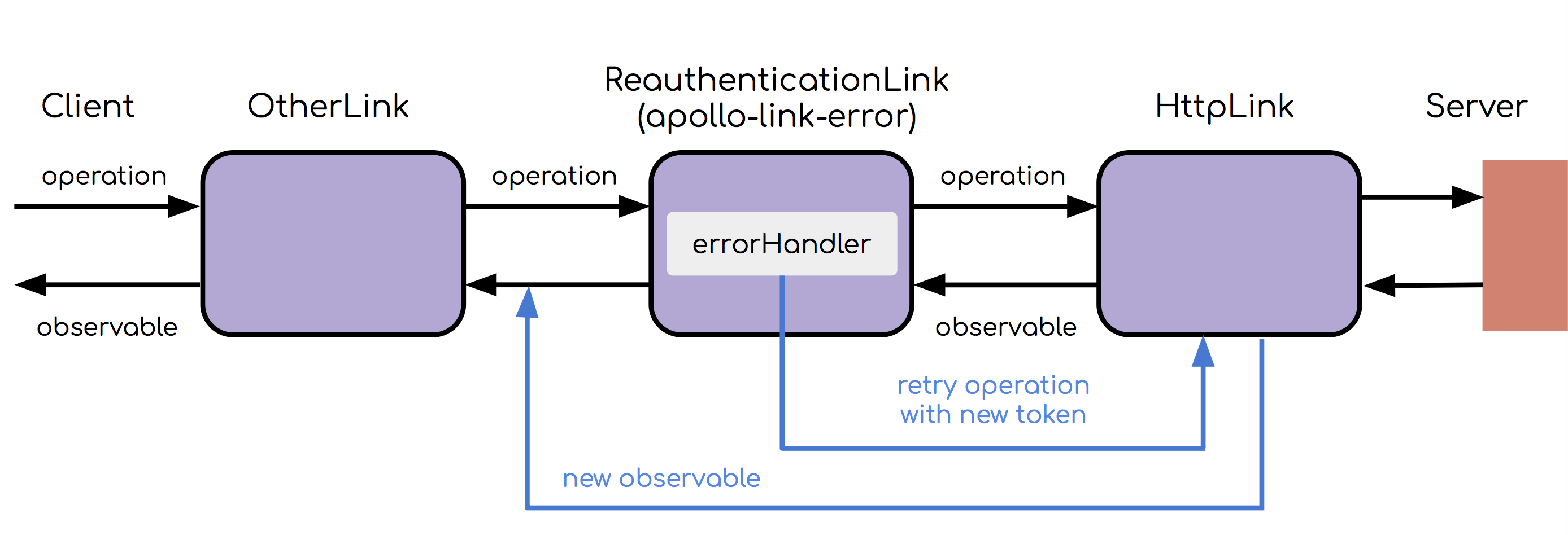
One caveat is that the errors in the new response, from retrying the request, do not get passed into the error handler again. This helps avoid being trapped in an endless request loop when you call forward() in your error handler.
Ignoring errors
If you want to conditionally ignore errors, you can set response.errors = null; within the error handler:
onError(({ response, operation }) => {
if (operation.operationName === "IgnoreErrorsQuery") {
response.errors = null;
}
});